Good Laboratory Practice Accreditation by the Standards Council of Canada

Who is the Standards Council of Canada (SCC)?
The Standards Council of Canada (SCC) is a Crown corporation established by an act of the Canadian Parliament in 1970 to foster and promote voluntary standardization in Canada. Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) accreditation of test facilities/sites by the SCC came into effect on January 1, 1987. On this date, the Standards Council of Canada officially recognized the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) Principles of Good Laboratory Practice and established a Compliance Monitoring Program to provide assurance to regulators, industry, and the public that the laboratory studies conducted at these facilities/sites are of high quality, reliable, and scientifically valid.
Who requires Good Laboratory Practice accreditation by the Standards Council of Canada?
GLP accreditation by the Standards Council of Canada is required for organizations conducting non-clinical health and environmental safety studies on products such as pharmaceuticals, pesticides, industrial chemicals, and medical devices. The accreditation ensures that the studies are conducted in compliance with the OECD principles of GLP, which covers a wide range of activities, including study design, conduct, monitoring, analysis, data collection, reporting, and archiving of study data and reports.
Is Standards Council of Canada (SCC) accreditation required for laboratory bioanalysis in clinical research?
While Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) specifically pertains to non-clinical studies, clients in clinical research still value GLP accreditation as a demonstration of a laboratory’s commitment to quality and compliance with established standards. Clients view GLP accreditation as an indicator of the laboratory’s ability to generate reliable and accurate data, which is also essential for the success of clinical studies.
What about EMA, Anvisa and WHO, why is Standards Council of Canada accreditation of value to them?
EMA (European Medicines Agency), ANVISA (Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária), and WHO (World Health Organization) are regulatory bodies responsible for evaluating the safety, efficacy, and quality of medicines and medical products in their respective regions. The Standards Council of Canada accreditation of a laboratory demonstrates to such agencies that the laboratory has been independently evaluated by a recognized body and meets internationally recognized standards for competence and quality management systems. This provides confidence to the regulatory agencies that the data generated by the laboratory are reliable and can be used to support global regulatory submissions.
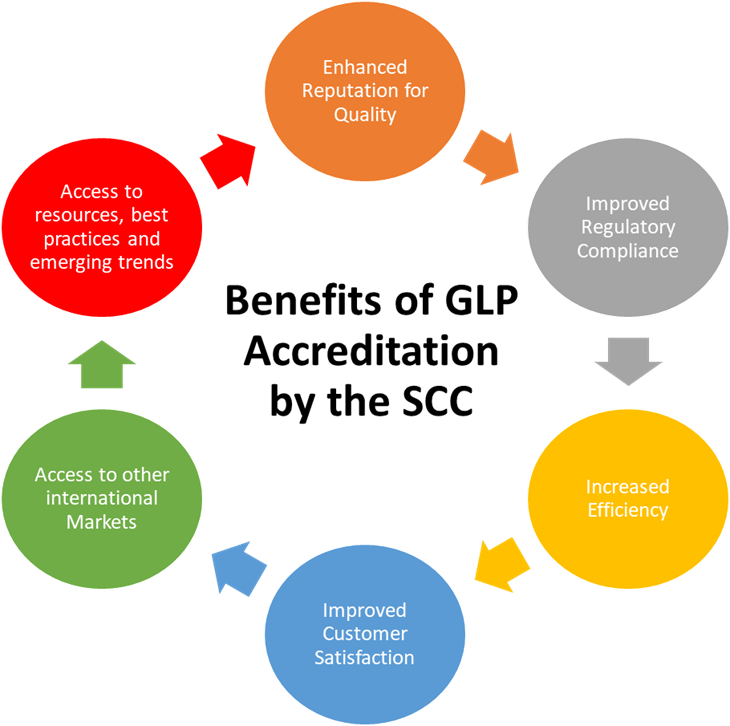
Benefits of Accreditation by the Standards Council of Canada (SCC)
Overall, Good Laboratory Practice accreditation can provide assurance to clients in clinical research that the laboratory, in conducting non-clinical studies, has implemented rigorous quality control measures, and is committed to generating high-quality data that can also support the clinical development program.
Roles and Responsibilities of key personnel for Good Laboratory Practice studies
The organizational structure of key personnel for a bioanalytical testing site may vary depending on the specific needs and goals of the organization. The key roles and responsibilities in a typical bioanalytical laboratory include but are not limited to the following:
- Test Facility/Site Management: Responsible for overseeing the entire laboratory operation, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, and maintaining the quality of test results, by ensuring:
-
- The facility/site has sufficient calibrated and maintained equipment and other materials and supplies for the timely and proper conduct of the study.
- The facility/site has adequate rooms or areas to prevent contamination or sample mix-ups.
- The assignment of a study director, or in the case of a multi-site study a Principal Investigator, who is appropriately trained and experienced to supervise the delegated phase of the study.
- The facility/site has sufficient qualified study personnel with adequate education, training, and experience, and maintain a record of such qualifications.
- That appropriate SOPs are established and followed. Approves all original and revised SOPs and maintains a historical list of SOPs.
- That an individual is identified responsible for the archive.
- That there is an independent QA program established with personnel to assure the study is performed in accordance with the principles of Good Laboratory Practice.
- The maintenance of the master schedule for Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) studies.
2. Study Director: Is the single point of study control, responsible for the scientific/technical conduct of the study and for its final report. For multisite studies, this may be delegated to the principal investigator. Responsibilities include:
-
- Approval of the study plan and any amendments, and make sure it is available to study personnel and QA.
- Ensure the details specified in the study plan are followed.
- Assess any impact of any deviations, take appropriate corrective actions, and acknowledge any deviations.
- Ensure all raw data are fully documented and recorded.
- Sign the final report and accept responsibility that the data and that the study complied with the principle of Good Laboratory Practice.
- At the end of the study ensure that study plan, study raw data and final report and supporting documentation are achieved.
3. Study Personnel:
-
- Generate analytical test results in compliance with current SOPs, protocols, study plans and applicable Good Laboratory Practice regulations.
- Record raw data promptly and accurately and in compliance with the OECD Principles of Good Laboratory Practice.
- Document and communicate any deviations to these instructions directly to the Study Director/Principal Investigator
- Exercise health precautions to minimize risk to themselves and to ensure the integrity of the study.
4. Quality Assurance Unit: The Quality Assurance (QA) Unit is responsible for ensuring that the laboratory complies with Good Laboratory Practice regulations and meets the quality standards set out by the organization. The QA Unit should be independent from and not be involved in the conduct of the laboratory study conduct.
-
- Maintain copies of approved study plans
- Conduct, record and retain records of inspections (study-based, facility-based, process-based)
- Inspect the final report and confirm that methods, procedures, and observations accurately describe and reflect the raw data of the studies.
- Report inspection results to study director, Principal investigator, and Laboratory management when applicable.
- Prepare and sign a QA statement to be included in the study report to describe the phase of the study that were inspected and to confirm that the final report reflects this raw data.
What is the process of getting certification/accreditation by the Standards Council of Canada (SCC)?
The audit process may vary depending on the specific requirements of the GLP regulations and the type of facility being audited. In general, the process includes but is not limited to the following:
- Notification and scheduling: The Standards Council of Canada will send out a document to the facility called the Annual Study Declaration, whereby the test site/facility provides the master schedule for each year, and after which a date for the inspection will be scheduled based on mutual availability.
- Pre-audit documentation review: Prior to the audit, the Standards Council of Canada will review the facility’s Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), and other relevant documentation (organization chart, facility floor plan) to ensure compliance with GLP regulations.
- On-site audit: The Standards Council of Canada auditor will conduct an on-site inspection of the facility to assess compliance with GLP regulations. The auditor will review procedures, protocols, and records, as well as observe laboratory activities against organizational SOPs and Good Laboratory Practice regulations.
- Audit report: Following the audit, the Standards Council of Canada auditor will prepare a “Finding report” detailing any non-conformances identified during the audit.
- Corrective and preventive action plan: The facility is required to prepare a Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) plan in response to any non-conformances identified in the finding report. The CAPA plan should include steps to address the non-conformances and prevent future recurrence of similar issues,
- Follow-up audit: The Standards Council of Canada may conduct a follow-up audit to ensure that the facility has taken corrective actions and continues to follow GLP regulations.
- Certification/Accreditation: If the facility is found to be following GLP regulations, the Standards Council of Canada will issue a certificate of compliance.
- List of accredited bodies are reported on the Standards Council of Canada website.

Why Choose BioPharma Services?
BioPharma services Inc. (BioPharma Services) is a full service CRO that launched its bioanalytical Laboratory in 2011. The laboratory uses LC-MS/MS techniques in quantitative small molecule bioanalysis to support non-clinical Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) and clinical research studies and has developed validated more than 250 bioanalytical methods. BioPharma Services has a strong regulatory inspection history from global agencies (FDA, EMA, ANVISA, EMA, WHO, MHRA).
BioPharma Services had its 1st inspection by the Standards Council of Canada in 2015, after which it successfully received SCC Certificate of Accreditation. Since 2015, the bioanalytical site has preformed bioanalytical services to support non-clinical studies for a variety of proprietary drugs. The conduct of applicable studies has been audited by the SCC every 2 years, and BioPharma Services has successfully retained its GLP accreditation status. You can find BioPharma Service’s full Regulatory Inspection History Here.
Good Laboratory Practice accreditation by the Standards Council of Canada recognizes that Biopharma Services Inc. has demonstrated competence and compliance with the standard’s requirements for quality management and technical operations related to how laboratory studies are planned, performed, monitored, recorded, reported, and retained (archived).
Written by: Dr. Nicola Hughes and Vaideki Dharmaratnam
BioPharma Services, Inc., a Think Research Corporation and clinical trial services company, is a full-service Contract Clinical Research Organization (CRO) based in Toronto, Canada, specializing in Phase 1 clinical trials 1/2a and Bioequivalence clinical trials for international pharmaceutical companies worldwide. BioPharma has clinical facilities both in the USA and Canada with access to healthy volunteers and special populations.