Atypical pharmacokinetic profiles observed with dasatinib reference listed drug product in bioequivalence studies
PRESENTED TO: BioPharma Services Inc., Toronto, Ontario, Canada
PRESENTED BY: R. Chandani, J. He, F. Trabelsi
PURPOSE
Dasatinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that is primarily indicated for the treatment of patients diagnosed with a form of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) in chronic phase. While there are several strengths of dasatinib available for prescription use, the recommended therapeutic dose for chronic phase CML is 100 mg once per day and for accelerated phase CML is 140 mg per day, which is also the highest strength available on the USA and EU markets.
The FDA draft guidance on Dasatinib for bioequivalence studies recommends 1 fasted, and 1 fed crossover study with the dosage of a 100 mg tablet administered via oral route in normal healthy volunteers (NHV). The EMA dasatinib product specific bioequivalence guidance recommends only a fasted single dose crossover study in NHV following a 140 mg dose, the highest strength available on the EU market.

RESULT(S)
Pooled systemic exposure data of the four 2-way cross-over studies following a 1 x 140 mg single dose of dasatinib, demonstrated approximately 5.22% of subjects had anomalously low plasma concentration and AUC values, relative to the population mean (i.e. less than 10% of the population mean).
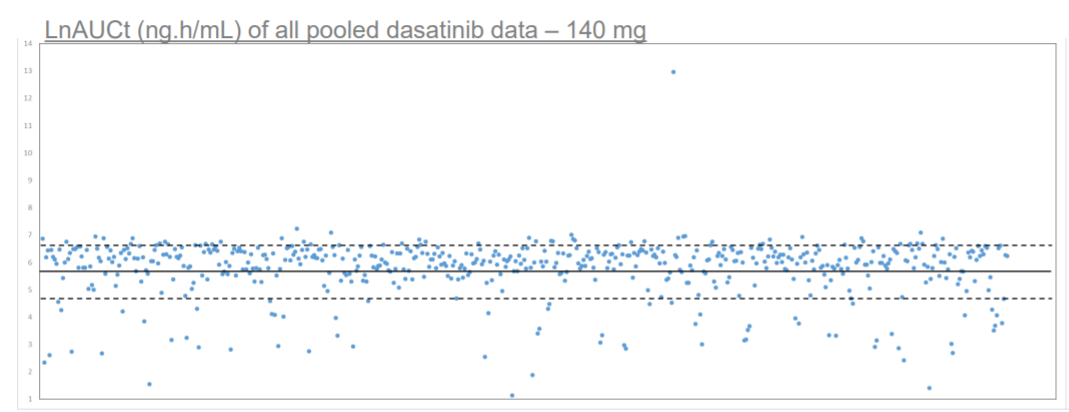
Scatter plot depicting distribution of individual LnAUCt values of individual subjects within NHV dosed with dasatinib RLD. Data has been pooled from several dasatinib 140 mg pivotal studies. Solid line depicts mean LnAUCt value of 5.78, segmented line depicts 1 standard deviation of 1.04. Image demonstrates that a significant portion of subjects express abnormally low AUCt of the RLD
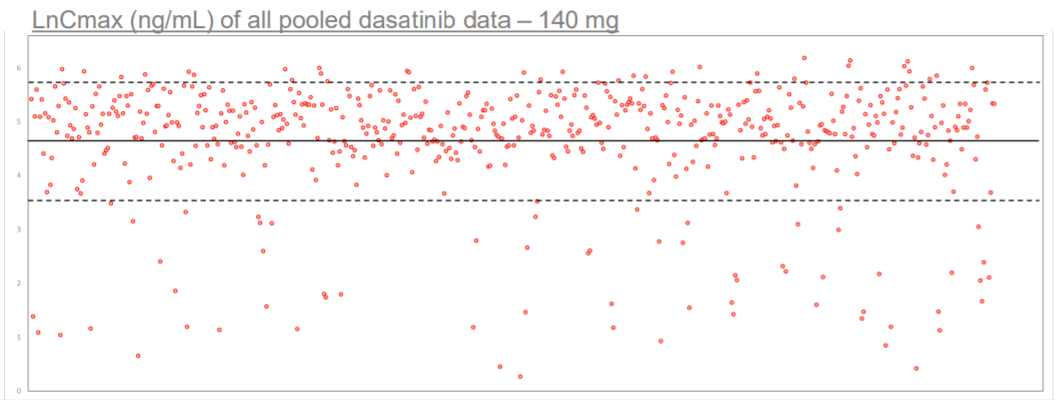
Scatter plot depicting distribution of individual LnCmax values of individual subjects within NHV dosed with dasatinib RLD. Data has been pooled from several dasatinib 140 mg pivotal studies. Solid line depicts mean LnCmax value of 4.65, segmented line depicts 1 standard deviation of 1.09. Image demonstrates that a significant portion of subjects express abnormally low Cmax of the RLD
For EU submission studies, EU regulation allows to exclude data from subjects demonstrating AUC values less than 5% of the mean AUC value, calculated upon exclusion of their respective individual data. Approximately 3.5% – 7.5% of subject data were excluded from the PK stats analysis in each study; this surmounted to a 4.6% rate of data exclusion from the pooled data set.
Overall very high-Intra subject variability was observed on AUCt, 40-50%, and on Cmax, 70-80%.
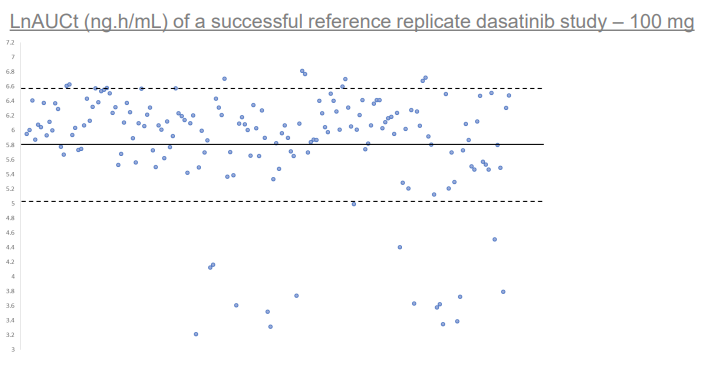
Scatter plot depicting distribution of individual LnAUCt values of individual subjects within NHV dosed with 100 mg dasatinib RLD. Solid line depicts mean LnAUCt value of 5.82, segmented line depicts 1 standard deviation of 0.78. Image demonstrates that a significant portion of subjects express abnormally low AUCt of the RLD
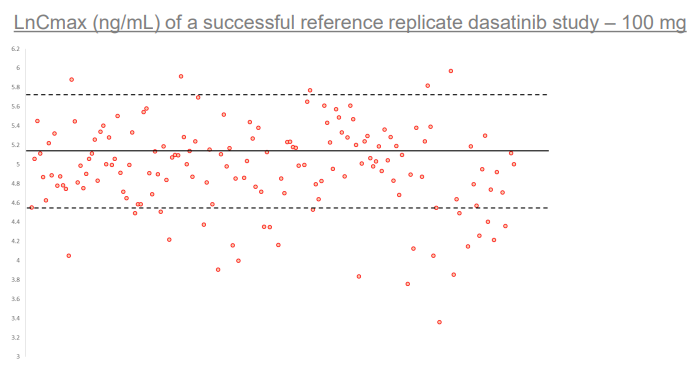
Scatter plot depicting distribution of individual LnCmax values of individual subjects within NHV dosed with 100 mg dasatinib RLD. Solid line depicts mean LnCmax value of 4.64, segmented line depicts 1 standard deviation of 1.09. Image demonstrates that a significant portion of subjects express abnormally low Cmax of the RLD
METHOD(S)
It was noted that the dasatinib reference listed drug (RLD) demonstrated very high ISCV within in-house clinical studies, as well as several instances of anomalous absorption and systemic exposure
• Objective of this poster is to discuss anomalous exposure profiles seen in small and inconsistent proportion of the panel within in-house dasatinib clinical studies
• 6 pivotal studies
• 1 reference replicate study = 100 mg
• 2 reference replicate studies = 140 mg
• 3 single dose two-way cross-over studies = 140 mg
• Fasted conditions
• 100 mg or 140 mg tablet strength
• Normal healthy volunteers (NHV)
• 1 week washout
• No concomitant consumption of CYP3A4 inducers/inhibitors that would interfere with metabolism of dasatinib
• Plasma concentration data resulting from dose administration of only RLD to NHV from all in-house studies pooled together
• Pooled data set (140 mg) and actual data set (100 mg) utilized in an in-depth analysis to further investigate trends and anomalous profiles observed following dasatinib RLD administration in BE studies
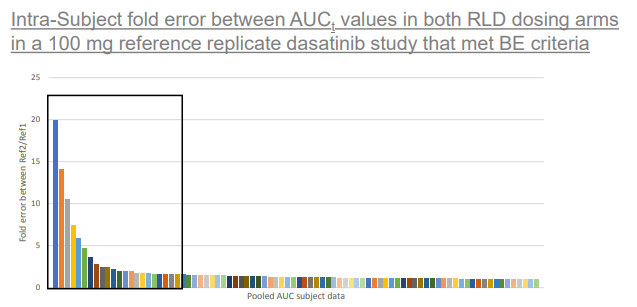
This image depicts the fold error demonstrated within individual subjects when comparing their respective AUCt values between 2 RLD dosing arms in 4 way fully replicate studies. Up to 20 times fold error can be seen between RLD dasatinib AUC values in a given subject. Values contained within the black box are >1.5 fold difference.
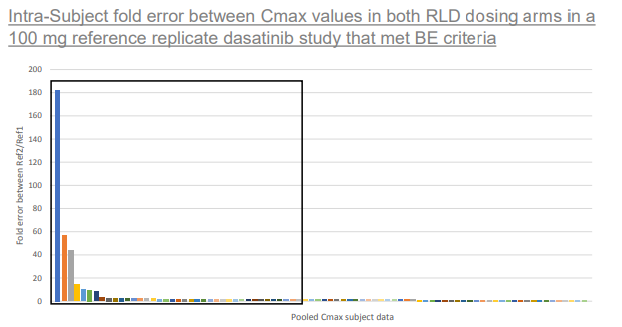
This image depicts the fold error demonstrated within individual subjects when comparing their respective Cmax values between 2 RLD dosing arms in 4 way fully replicate studies. Up to 182 times fold error can be seen between RLD dasatinib Cmax values in a given subject. Values contained within the black box are >1.5 fold difference.
RESULT(S)
Study conclusion
• Overall the RLD product has consistently demonstrated erratic pharmacokinetic exposure profiles in 3.5% – 7.5% in every in-house study, as well as very high ISCV. This could very likely be due to:
• Excipient solubility factors associated with the RLD formulation
• pH-dependent solubility: Dasatinib is a BCS Class
II. For Class II drugs inadequate and pH dependent dissolution contributes to the variability in absorption.
• Fluctuating gastric pH levels that may affect dasatinib absorption
• For EU studies approximately 4.5% of subject data was excluded due to anomalous profile regulations
• FDA outlier test carries a far more stringent criteria for PK data exclusion as compared to the EMA 5% rule; As a result, far fewer individual subject data sets would qualify for data exclusion based on the results of a studentized residuals outlier test.
• There were no recognizable trends associated with dosage strength or population demographics (i.e. race, age, weight etc.)
Future considerations
• Evaluate gastric pH influence on dasatinib absorption after an overnight fast, before dosing
• i.e. using Smart Pill technology
• Evaluate reference listed drug for variability, pH dependant solubility, and consistency of absorption
• Incorporate additional buffer into sample size consideration to compensate for expected portion of anomalous PK results



