The Key Role Of Quality Control in Clinical Trials

What is Quality Control in Clinical Trials (QC)?
Quality Control in human clinical trials means the procedures which ensure the protection of human subjects from research risk, reliability of the data, and thereby assuring internal consistency. This has been developed since the 1970s in the US, by establishing various regulations, which are now called GCP.
Good clinical practice (GCP):
It is an international ethical and scientific quality standard for designing, conducting, recording, and reporting trials that involve the participation of human subjects. Since 1997, the ICH-GCP E6(R2) guidelines have been a requirement for conducting human clinical trials, which should be used as documentation to the authorities.
GCP clinical trials adherence to quality standards during the clinical trial process assures that the data and the reported results are credible and accurate and that the rights, integrity, and confidentiality of the trial subjects are protected.
The Quality Challenge
The ongoing challenge in managing the quality of clinical data is to continually monitor data collection procedures and data management practices at every level of the study. Maintaining accuracy and quality throughout clinical studies is a continual, dynamic process.
Although study requirements are carefully set forth initially in detailed documents such as an approved clinical protocol, A clinical trial data management plan, and an accompanying project plan, expectations and requirements can change during a study. This ongoing process requires revising mechanisms and communicating these revisions clearly to all investigators and support staff.
Operational techniques and activities within the QC system to verify the quality requirements’ fulfillment for the trial-related activities.
How do we ensure quality control in clinical trials?
- Implementing standard processes/procedures (SOPs).
- Effective GCP clinical trial training.
- Refresher training to build quality into clinical research.

When does Quality Control in clinical trials get implemented?
A Quality Control in clinical trials plan should be developed for each operational step of the clinical research study. The plan should define standards against which QC will conduct. During the study design phase, QC personnel provide an independent review of the approved proposed protocol.
The Quality Control in clinical trials plan includes a comparison of the study’s CRF to the objective outlined in the protocol to ensure that it’s designed to collect all necessary data. A requirement to review CRF completion guidelines is also an element of the QC plan.
It should be done continuously before conducting the study and even after the study is done. QC plays an important role in reviewing and checking all source documents and the data generated from the study.
All quality systems must document work instructions, tolerances, and policies. Within our GxP environment, the Quality Control in clinical trials plan is required to have written work instructions and standard operating procedures (SOPs). These documents are used to define how each process, task, instrument calibration, etc. will be carried out.
These documents form the core of the quality system. The importance of getting them accurately reflects what has been done can not be over-emphasized.
Another aspect of this function of quality system building is the control of such documents. It is of paramount importance that staff is not using outdated, replaced procedures, or unofficial copies. This task falls on the QC specialist with the support of QA to make sure that this control over these documents is implemented.
Quality control steps must be considered while conducting the clinical trial:
1. Before starting the clinical trial.
- Qualifications of investigator and research staff, IRB submission
- Site/facilities vs. Protocol requirements
- Protocol vs. Informed Consent
- Protocol vs. Case Report forms.
The quality controller must make sure that all study procedures are implemented correctly. This will ensure that a set of independent eyes are cast over the study project to help spot any unforeseen problems. QC should look for trends & flows in the process and have corrective & preventive action accordingly. It is this cyclic nature of QC that must be introduced as part of QC culture in any organization.
2. During the clinical trial:
- Throughout the trial, monitoring, and audit are particularly important to assure quality.
- In process review which can be also named a live review, ensures that all clinical procedures are conducted as per (SOPs), and study clinical trial protocols, also it examines data capture, data recording, and protocol compliance.
- Quality planning includes all work we do to organize and layout a plan to deliver Complete, Consistent, Correct, Feasible, Traceable, and unambiguous raw data.
Another aspect of this function of quality system building is the control of such documents. It is of paramount importance that staff is not using outdated, replaced procedures, or unofficial copies. This task falls on the QC specialist with the support of QA to make sure that this control over these documents is implemented.
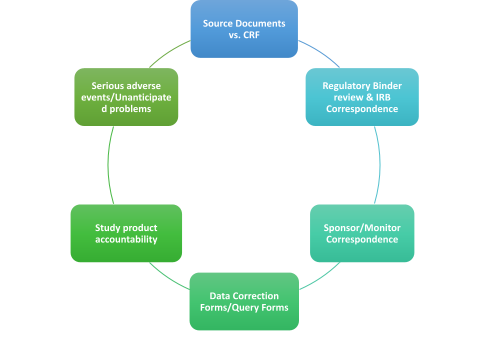
3. The end of the clinical trial and the Study clean-up
- Data Base review:
- Source documents/Clinical study reports.
- Safety & efficacy summary
- SAE’s, follow up on the adverse events until resolution.
- Final Study report.
Quality surveillance continues after the trial has ended and plays an important role in ensuring that Data presented in tables, listings, and graphs (TLGs) accurately present the raw data that was generated from the clinical trial.
The Data reported in the clinical study report (CSR) is the data analyzed. Finally, that all aspects of the data management process are compliant with SOPs & GCPs.
All observations during clinical trials quality control review are documented in the QC report
- The QC report must be responded to in a timely manner to ensure that Data correction and clarification happened in a timely manner & in compliance with GDP.
- The QC report must be backed up by audit-trailed raw data.
- All findings are addressed in a timely manner.
- Perform in-process review to check all study procedures, calibrated equipment, and delegation of the staff.
- No Typographical errors exist.
Protocol and Study Plan Compliance Check
Raw Data to Tables Check:
-
- Ensure that each data reported has source-data verification.
- Ensure that QC acceptance criteria have been met.
- Check summary statistics of all tables in QC data.
Summary Check:
-
- Ensure that data summary statistics in the text match those in tabulated data.
- Check the precision of reporting values (Decimals, significant digits, and rounding).
- Check that the overall results support the conclusions of the report.
Consistency Check:
-
- Check table titles for accuracy.
- Check that footnotes are consistent with contractions used in the QC report.
- Check all table figures for links to report with page numbers.
- Check that all externally supplied documentation is compliant with the study protocol. (Certificate of analysis, batch numbers, expiration dates for the related IMP)
In-process review:
-
- Check that subjects that are enrolled in the clinical trial are deemed eligible by the principal investigator.
- Check that clinical trial procedures are implemented according to protocol.
- Check that equipment is calibrated, and the calibration is not expired.
- Ensure that all staff participating in the study are delegated by the principal investigator.
- Ensure that all the raw data generated are documented by the delegated staff.
Typographic Errors:
-
- Check that all documentation is complete.
- Check page numbering is consecutive, and that no blank pages exist & all pages are filed in the study file.
- Check the sponsor’s reference number and cross-reference with the protocol.
- Verify that the unique report identification number is in place
Why Choose BioPharma Services for your next Clinical Trial Protocol Development?
Compliance with quality requirements is the cornerstone of a scientifically valid and ethically sound clinical trial. The twin objectives of quality-Data integrity and subject protection-can be met by a systemic approach to the whole process of conducting first in human clinical trials. BioPharma Services will ensure that all aspects of Quality Control in clinical trials are above industry standards. Don’t believe us, fill out a Contact Form and discuss with an expert team member that will guide you through the BioPharma difference.
Find out why BioPharma might be the right partner for you! Learn more about BioPharma Services and the wide array of bioanalytical services we provide.
BioPharma Services, Inc., a Think Research Corporation and clinical trial services company, is a full-service Contract Clinical Research Organization (CRO) based in Toronto, Canada, specializing in Phase 1 clinical trials 1/2a and Bioequivalence clinical trials for international pharmaceutical companies worldwide. BioPharma has clinical facilities both in the USA and Canada with access to healthy volunteers and special populations.



